Managing Update Conflicts in Bayou,
a Weakly Connected Replicated Storage System
Douglas B. Terry, Marvin M. Theimer, Karin Petersen, Alan J. Demers,
Mike J. Spreitzer and Carl H. Hauser
Computer Science Laboratory
Xerox Palo Alto Research Center
Palo Alto, California 94304 U.S.A.
Abstract
Bayou is a replicated, weakly consmtent storage system designed for a mobile computing environment that includes porta-
ble machines with less than ideal network connectivity. To maxi- mize availabdity, users can read and write any accessible replica.
Bayou’s design has focused on supporting apphcation-specific mechanisms to detect and resolve the update conflicts that natu-
rally arise in such a system, ensuring that replicas move towards
eventual consistency, and defining a protocol by which the resolu- tion of update conflicts stabilizes, It includes novel methods for confhct detection, called dependency checks, and per-write con- flict resolution based on client-provided merge procedures. To
guarantee eventual consistency, Bayou servers must be able to roll- back the effects of previously executed writes and redo them according to a global serialization order. Furthermore, Bayou per-
mits clients to observe the results of all writes received by a server, mchrding tentative writes whose conflicts have not been ultimately resolved. This paper presents the motivation for and design of these mechanisms and describes the experiences gained with an
initial implementation of the system.
1. Introduction
The Bayou storage system prowdes an mfrastrtrcture for col-
laborative applications that manages the conflicts introduced by concurrent activity while relying only on the weak connectivity available for mobile computing. The advent of mobile computers,
in the form of laptops and personal digital assistants (PDAs) enables the use of computational facilities away from the usual work setting of users. However, mobile computers do not enjoy the
connectivity afforded by local area networks or the telephone sys- tem. Even wireless media, such as cellular telephony, will not per-
mit continuous connectivity until per-mmute costs decline enough
to justify lengthy connections. Thus, the Bayou design requires
only occasional, patr-wise communication between computers.
This model takes into consideration characteristics of mobile com-
puting such as expensive connection time, frequent or occasional disconnections, and that collaborating computers may never be all connected simultaneously [1, 13, 16].
The Bayou architecture does not include the notion of a “dis- connected” mode of operation because, in fact, various degrees of
Permission to make digital/hard copy of part or all of this work for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed for profit or commercial advantage, the copyright notice, the title of the publication and its date appear, and notiea is given that copying is by permission of ACM, Inc. To copy otherwise, to republish, to post on servers, or to recktribute to lists, requires prior specific permission aodlor a fee.
SIGOPS ’95 12/95 CO, USA 01995 ACM 0-89791-71 5-4/9510012…$3.50
“connectedness” are possible. Groups of computers may be pafii-
tioned away from the rest of the system yet remain connected to each other. Supporting disconnected workgroups is a central goal
of the Bayou system. By relying only on pair-wise communication
in the normal mode of operation, the Bayou design copes with arbitrary network connectivity.
A weak connectivity networking model can be accommodated only with weakly consistent, replicated data. Replication is
reqtured since a single storage site may not be reachable from
mobile clients or within disconnected workgroups. Weak consis-
tency is desired since any replication scheme providing one copy serializablhty [6], such as reqturing clients to access a quorum of replicas or to acquire exclusive locks on data that they wish to
update, yields unacceptably low write availability in par-btioned
networks [5]. For these reasons, Bayou adopts a model in which chents can read and write to any replica without the need for explicit coordination with other rephcas. Every computer eventu- ally receives updates from every other, either directly or indirectly, through a chain of pair-wise interactions.
Unhke many previous systems [12, 27], our goal m designing
the Bayou system was not to provide transparent rephcated data support for existing file system and database applications. We believe that applications must be aware that they may read weakly
consistent data and also that their wrrte operations may conflict with those of other users and applications. Moreover, applications
must be revolved m the detection and resolution of conflicts since
these naturally depend on the semantics of the application. To this end, Bayou provides system support for applicatlon-
specific confllct detection and resolution. Previous systems, such
as Locus [30] and Coda [17], have proven the value of semantic conflict detection and resolution for file directories, and several systems are exploring conflict resolution for file and database con- tents [8, 18, 26]. Bayou’s mechamsms extend this work by letting
applications exploit domain-specific knowledge to achieve auto-
matic conflict resolution at the granularity of individual update
operations without compromising security or eventual consistency. Automatic conflict resolution is highly desirable because lt
enables a Bayou replica to remam available. In a replicated system
with the weak connectiwt y model adopted by Bayou, conflicts may be detected arbitrarily far from the users who introduced the
conflicts. Moreover, conflicts may be detected when no user is present. Bayou does not take the approach of systems that mark conflicting data as unavadable until a person resolves the conflict. Instead, clients can read data at all times, including data whose
conflicts have not been fully resolved either because human inter- vention M needed or because other conflicting updates may be propagating through the system. Bayou provides interfaces that
make the state of a replica’s data apparent to the application. The contributions presented in this paper are as follows: we
introduce per-update dependency checks and merge procedures as
J.72
a general mechamsm for application-specific conflict detection and
resolution; we define two states of an update, committed and tenta-
tive, which relate to whether or not the conflicts potentially intro-
duced by the update have been ultimately resolved; we present
mechanisms for managing these two states of an update both from
the perspective of the clients and the storage management require-
ments of the replicas; we describe how replicas move towards
eventual consistency; and, finally, we discuss how security is pro- vided in a system like Bayou.
2. Bayou Applications
Tbe Bayou replicated storage system was designed to support a
variety of non-real-time collaborative applications, such as shared
calendars, mad and bibliographic databases, program develop- ment, and document editing for disconnected workgroups, as well
as applications that might be used by individuals at different hosts
at different times. To serve as a backdrop for the discussion in fol-
lowing sections, this section presents a quick overview of two applications that have been implemented thus far, a meeting room scheduler and a bibliographic database.
2.1 Meeting room scheduler
Our meeting room scheduling application enables users to reserve meeting rooms. At most one person (or group) can reserve
the room for any given period of time. This meeting room schedul- ing program M intended for use after a group of people have
already decided that they want to meet in a certain room and have determined a set of acceptable times for the meeting. It does not help them to determine a mutually agreeable place and time for the
meeting, it only allows them to reserve the room. Thus, it is a
much simpler application than one of general meeting scheduling. Users interact with a graphical interface for the schedule of a
room that indicates which times are already reserved, much like the display of a typical calendar manager. The meeting room
scheduling program periodically re-reads the room schedule and refreshes the user’s display. This refresh process enables the user to observe new entries added by other users. The user’s display might be out-of-date with respect to the confirmed reservations of
the room, for example when it is showing a local copy of the room
schedule on a disconnected laptop. Users reserve a time slot simply by selecting a free time period
and filling in a form describing the meeting that is being sched-
uled. Because the user’s display might be out-of-date, there is a
chance that the user could try to schedule a meeting at a time that was already reserved by someone else. To account for this possi-
bdity, users can select several acceptable meeting times rather than just one. At most one of the requested times will eventually be reserved.
A user’s reservation, rather than being immediately confirmed
(or rejected), may remain “tentative” for awhile. While tentative, a meeting may be rescheduled as other interfering reservations
become known. Tentative reservations are indicated as such on the display (by showing them grayed). The “outdatedness” of a calen-
dar does not prevent it from being useful, but simply increases the
likelihood that tentative room reservations will be rescheduled and
finally “committed” to less preferred meeting times. A group of users, although disconnected from the rest of the
system, can immediately see each other’s tentative room reserva-
tions if they are all connected to the same COPY of the meeting room schedule. If, instead, users are maintaining private copies on
their laptop computers, local communication between the machines will eventually synchronize all copies within the group.
2.2 Bibliographic database
Our second application allows users to cooperatively manage
databases of bibliographic entries. Users can add entries to a data-
base as they find papers in the library, in reference lists, via word
of mouth, or by other means. A user can freely read and write any
copy of the database, such as one that resides on his laptop. For the
most part, the database is append-only, though users occasionally
update entries to fix mistakes or add personal annotations.
As is common in bibliographic databases, each entry has a
unique, human-sensible key that is constructed by appending the
year in which the paper was published to the first author’s last
name and adding a character if necessary to distinguish between
multiple papers by the same author in the same year. Thus, the first paper by Jones et al, in 1995 might be identified as “Jones95” and subsequent papers as “Jones95b’, “Jones95c”, and so on,
An entry’s key 1s tentatively assigned when the entry is added.
A user must be aware that the assigned keys are only tentative and
may change when the entry is “committed.” In other words, a user
must be aware that other concurrent updaters could be trying to assign the same key to different entries. Only one entry can have
the key; the others will be assigned alternative keys by the system.
Thus, for example, if the user employs the tentatively assigned key
in some fashion, such as embedding it as a citation in a document, then he must also remember later to check that the key assigned when the entry was committed is in fact the expected one.
Because users can access inconsistent database copies, the same bibliograpblc entry may be concurrently added by different users with different keys. To the extent possible, the system detects
duplicates and merges their contents into a single entry with a sin-
gle key. Interestingly, this is an application where a user may choose to
operate in disconnected mode even if constant connectivity were
possible. Consider the case where a user is in a university library looking up some papers. He occasionally types bibliographic refer- ences into his laptop or PDA. He may spend hours m the library
but only enter a handful of references. He is not likely to want to keep a cellular phone connection open for the duration of his visit. Nor will he want to connect to the university’s local wireless net- work and subject himself to student hackers. He wdl more likely
be content to have his bibliographic entries integrated into his database stored by Bayou upon returning to his home or office.
3. Bayou’s Basic System Model
In the Bayou system, each data collection is replicated in full at
a number of servers. Applications running as clienrs interact with the servers through the Bayou application programming interface
(API), which is implemented as a client stub bound with the appli- cation. This API, as well as the underlying client-server RPC pro- tocol, supports two basic operations: Read and Wrife. Read operations permit queries over a data collection, while Write oper-
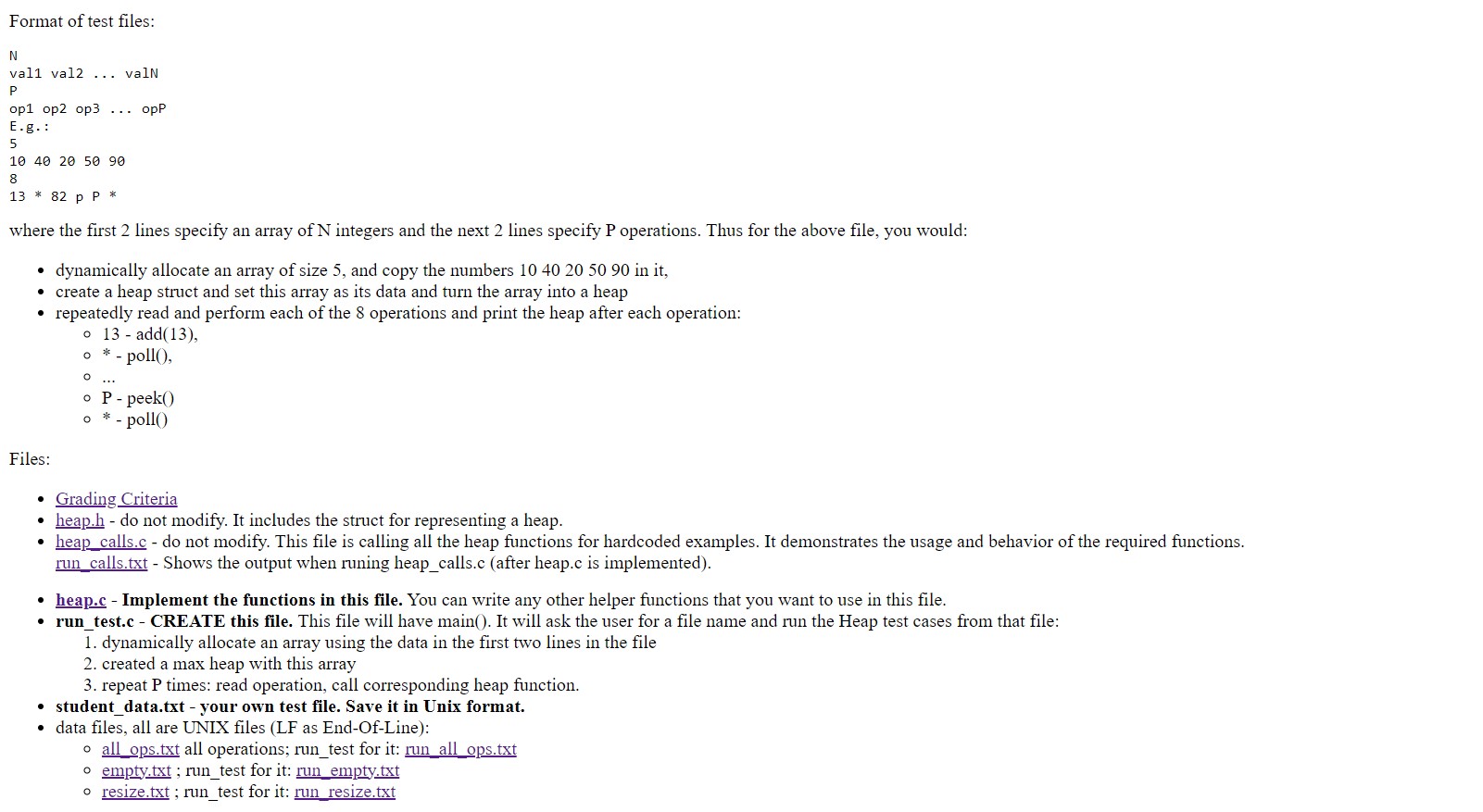
ations can insert, modify, and delete a number of data items in a collection. Figure 1 illustrates these components of the Bayou architecture. Note that a chent and a server may be co-resident on a
host, as would be typical of a laptop or PDA running in isolation.
Access to one server is sufficient for a client to perform useful work. The client can read the data held by that server and submit
Writes to the server. Once a Write is accepted by a server, the cli-
ent has no further responsibility for that Write. In particular, the client does not wait for the Write to propagate to other servers, In other words, Bayou presents a weakly consntent replication model with a read-uny/write-any style of access. Weakly consistent repli-
cation has been used previously for availability, simplicity and
scalability in a variety of systems [3, 7, 10, 12, 15, 19].
173
Anti-entropy
Figure 1. Bayou System Model
While individual Read and Write operations are performed at a
single server, clients need not confine themselves to interacting with a single server. Indeed, in a mobile computing environment,
switching bet ween servers is often desirable, and Bayou provides session guarantees to reduce client-observed inconsistencies when accessing different servers. The description of session guarantees has been presented elsewhere [29].
To support application-specific conflict detection and resolu-
tion, Bayou Writes must contain more than a typical file system write or database update. Along with the desired updates, a Bayou Write carries information that lets each server receiving the Write
decide if there is a conflict and if so, how to fix it. Each Bayou Write also contains a globally unique WriteID assigned by the server that first accepted the Write.
The storage system at each Bayou server conceptually consists of an ordered log of the Writes described above plus the data resulting from the execution of these Writes. Each server performs each Write locally with conflicts detected and resolved as they are
encountered during the execution. A server immediately makes the effects of all known Writes available for reading.
In keeping with the goal of requiring as little of the network as
possible, Bayou servers propagate Writes among themselves dur-
ing pair-wise contacts, called anti-entropy sessions [7]. The two
servers involved in a session exchange Write operations so that
when they are finished they agree on the set of Bayou Writes they
have seen and the order in which to perform them. The theory of epidemic algorithms assures that as long as the
set of servers is not permanently partitioned each Write will even-
tually reach all servers [7]. This holds even for communication patterns in which at most one pair of servers is ever connected at once. In the absence of new Writes from clients, all servers will eventually hold the same data. The rate at which servers reach con- vergence depends on a number of factors including network con- nectivity, the frequency of anti-entropy, and the policies by which
servers select anti-entropy partners. These policies may vary
according to the characteristics of the network, the data, and its servers. Developing optimal anti-entropy policies is a research topic in its own right and not further discussed in this paper.
4. Conflict Detection and Resolution
4.1 Accommodating application semantics
Supporting application-specific conflict detection and resolu- tion is a major emphasis in the Bayou design, A basic tenet of our
work is that storage systems must provide means for an application to specify its notion of a conflict along with its policy for resolving
conflicts. In return, the system implements the mechanisms for
reliably detecting conflicts, as specified by the application, and for
automatically resolving them when possible. This design goal fol- lows from the observation that different applications have different
notions of what it means for two updates to conflict, and that such conflicts cannot always be identified by simply observing conven- tional reads and writes submitted by the applications.
As an example of application-specific conflicts, consider the meeting room scheduling application discussed in Section 2.1. Observing updates at a coarse granularity, such as the whole-file level, the storage system might detect that two users have concur-
rently updated different replicas of the meeting room calendar and conclude that their updates conflict. Observing updates at a fine
granularity, such as the record level, the system might detect that
the two users have added independent records and thereby con-
clude that their updates do not conflict. Neither of these conclu-
sions are warranted. In fact, for this application, a conflict occurs
when two meetings scheduled for the same room overlap in time. Bibliographic databases provide another example of applica-
tion-specific conflicts. In this application, two bibliographic entries
conflict when either they describe different publications but have been assigned the same key by their submitters or else they describe the same publication and have been assigned distinct keys. Again, this definition of conflicting updates is specific to this
application. The steps taken to resolve conflicting updates once they have
been detected may also vary according to the semantics of the
application. In the case of the meeting room scheduling applica-
tion, one or more of a set of conflicting meetings may need to be
174
Bayou_Write (update, dependency_check, mergeproc) {
IF (DB_Eval (dependency_check. query) <> dependency_check.expected_result)
resolved_update = Interpret (mergeproc);
ELSE
resolved_update = update; DB_Apply (res~lved_up~ate);
}
Figure 2. Processing a Bayou Write Operation
Bayou_Write(
update = {insert, Meetings, 12/18/95, 1:30pm, 60min, “Budget Meeting”),
dependency_check = { query = “SELECT key FROM Meetings WHERE day= 12/18/95
AND start < 2:30pm AND end> l:30pm”,
expected_result = EMPTY},
mergeproc = {
alternates = {{12/18/95, 3:OOpm], {12/19/95, 9:30am]];
newupdate = {]; FOREACH a IN alternates {
# check fthere would be a conflict
IF (NOT EMPTY ( SELECT key FROM Meetings WHERE day = a.date AND start < a.time + 60min AND end > a.time))
CONTINUE; #no conflict, can schedule meeting at that time
newupdate = {insert, Meetings, a.date, a.time, 60min, “Budget Meeting”);
BREAK;
1 IF (newupdate = {]) #no alternate is acceptable
newupdate = {insert, ErrorLog, 12/18/95, 1:30pm, 60min, “Budget Meeting”];
) RETURN newupdate;}
Figure 3, A Bayou
moved to a different room or different time. In the bibliographic apphcation, an entry may need to be assigned a different unique key or two entries for the same publication may need to be merged
into one.
The Bayou system includes two mechanisms for automatic
conthct detection and resolution that are intended to support arbi-
trary applications: dependency checks and merge procedures. These mechanisms permit clients to indicate, for each individual
Write operation, how the system should detect conflicts involving
the Write and what steps should be taken to resolve any detected conflicts based on the semantics of the application. They were
designed to be flexlble since we expect that apphcations will differ appreciably in both the procedures used to handle conflicts, and, more generally, in their ability to deal with conflicts.
Techniques for semantic-based confhct detection and resolution have previously been incorporated into some systems to handle
special cases such as file directory updates. For example, the
Locus [30], FICUS [12], and Coda [17] distributed file systems all
include mechanisms for automatically resolving certain classes of
conflicting directory operations. More recently, some of these sys-
tems have also incorporated support for “resolver” programs that reduce the need for human intervention when rmnlvlng other types of file confllcts [18. 26]. Omcle’s symmetric rephcatlon product
also includes the notion of application-selected resolvers for rela- tional databases [8]. Other systems. llke Lotus Notes [ 15]. do not
Vrite Operation
provide application-specific mechanisms to handle conflicts, but rather create multiple versions of a document, file, or data object when conflicts arise. As wdl become apparent from the next cou-
ple of sections, Bayou’s dependency checks and merge procedures
are more general than these previous techniques.
4.2 Dependency checks
Application-specific conflict detection is accomplished in the
Bayou system through the use of dependency checks. Each Write
operation includes a dependency check consisting of an applica- tion-supplied query and its expected result. A conflict is detected if
the query, when run at a server against its current copy of the data, does not return the expected result. This dependency check 1s a precondition for performing the update that is mchtded in the
Write operation. If the check fails, then the requested update is not
performed and the server revokes a procedure to resolve the detected confllct as outlined in Figure 2 and discussed below.
As an example of apphcauon-detined conflicts, Figure 3 pre- sents a sample Bayou Write operat]on that might be submitted by
the meeting room scheduhng application. This Write ottempts to reserve an hour-long time slot. It includes a dependency check with a single query. written in an SQL-like language, that return>
information about any pre~ Iousl> reserved meetings th:~t o] erl:ip with this ume slot It expects the quer! to return m empt> wt
175
Bayou’s dependency checks, like the version vectors and times-
tamps traditionally used in distributed systems [12, 19, 25, 27], can
be used to detect Write-Write confhcts. That is, they can be used to
detect when two users update the same data item without one of them first observing the other’s update. Such conflicts can be
detected by having the dependency check query the current values of any data items being updated and ensure that they have not changed from the values they had at the time the Write was sub-
mitted, as M done in Oracle’s rephcated database [8]. Bayou’s dependency checking mechanism is more powerful
than the traditional use of version vectors since it can also be used
to detect Read-Write conflicts. Specifically, each Write operation
can explicitly specify the expected values of any data items on which the update depends, including data items that have been
read but are not being updated. Thtrs, Bayou chents can emulate
the optimistic style of concurrency control employed in some dis-
tributed database systems [4, 6]. For example, a Write operation that installs a new program binary file might only include a depen-
dency check of the sources, including version stamps, from which It was derived. Since the binary does not depend on lts previous value, this need not be included.
Moreover, because dependency queries can read any data in the
server’s replica, dependency checks can enforce arbitrary, muhl –
item integrity constraints on the data. For example, suppose a Write transfers $100 from account A to account B. The applica-
tion, before issuing the Write, reads the balance of account A and
discovers that it currently has $150. Traditional optimistic concur- rency control would check that account A still had $150 before
performing the requested Write operation. The real requirement, however, is that the account have at least $100, and this can easily be specified in the Write’s dependency check. Thus, only if con- current updates cause the balance in account A to drop below $100 will a conflict be detected.
4.3 Merge procedures
Once a conflict is detected, a merge procedure is run by the
Bayou server in an attempt to resolve the conflict. Merge proce-
dures, included with each Write operation, are general programs written m a high-level, interpreted language. They can have
embedded data, such as application-specific knowledge related to
the update that was being attempted, and can perform arbitrary Reads on the current state of the server’s replica. The merge proce-
dure associated with a Write M responsible for resolving any con- flicts detected by its dependency check and for producing a rewsed
update to apply. The complete process of detecting a conflict, nm- ning a merge procedure, and applying the revised update, shown in Figure 2, is performed atomically at each server as part of execut- ing a Write.
In principle, the algorrthm m Figure 2 could be imbedded in each merge procedure, thereby ehrninating any special mecha-
nisms for dependency checking. This approach would require
servers to create a new merge procedure interpreter to execute each Wrrte, which would be overly expensive. Supporting dependency
checks separately allows servers to avoid running the merge proce- dure in the expected case where the Write does not introduce a conflict.
The meeting room scheduling apphcatlon provides good exam-
ples of conflict resolution procedures that are specific not only to a
particular application but also to a patlcular Write operation. In this application, users, well aware that their reservations may be
invalidated by other concurrent users, can specify alternate sched-
uling choices as part of their original scheduling updates. These alternates are encoded in a merge procedure that attempts to
reserve one of the alternate meeting times if the original time is found to be in confhct with some other previously scheduled meet-
ing. An example of such a merge procedure is dlustrated m Figure
3. A different merge procedure altogether could search for the next
available time slot to schedule the meeting, which is an option a user might choose if any time would be satisfactory.
In practice, Bayou merge procedures are written by application
programmers m the form of templates that are instantiated with the appropriate details filled in for each Write. The users of apphca- tions do not have to know about merge procedures, and therefore
about the internal workings of the applications they use, except when automatic confhct resolution cannot be done.
In the case where automatic resolution is not possible, the
merge procedure wdl still run to completion, but is expected to produce a revised update that logs the detected conflict in some
fashion that will enable a person to resolve the conflict later. To
enable manual resolution, perhaps using an interactive merge tool
[22], the conflicting updates must be presented to a user in a man-
ner that allows him to understand what has happened. By conven- tion, most Bayou data collections include an error log for
unresolvable conflicts. Such conventions, however, are outside the domain of the Bayou storage system and may vary according to
the application. In contrast to systems like Coda [18] or Ficus [26] that lock
individual files or complete file volumes when contlcts have been
detected but not yet resolved, Bayou allows replicas to always remain accessible. This permits chents to continue to Read previ- ously written data and to continue to issue new Wrttes. In the
meeting room scheduling application, for example, a user who
only cares about Monday meetings need not concern himself with scheduling conflicts on Wednesday. Of course, the potential draw-
back of this approach is that newly issued Writes may depend on data that M in conflict and may lead to cascaded conflict resolution.
Bayou’s merge procedures resemble the previously mentioned
resolver programs, for which support has been added to a number
of replicated file systems [18, 26]. In these systems, a file-type- specific resolver program is run when a version vector mismatch is detected for a file. This program ]s presented with both the current and proposed tile contents and it can do whatever it wishes in order
to resolve the detected conflict. An example is a resolver program
for a binary file that checks to see if it can find a specltication for how to derive the file from its sources, such as a Unix makefile,
and then recompiles the program in order to obtain a new, “resolved” value for the file. Merge procedures are more general since they can vary for individual Write operations rather than
being associated with the type of the updated data, as illustrated
above for the meeting room scheduling application.
5. Replica Consistency
While the replicas held by two servers at any time may vary in
their contents because they have received and processed d] fferent Writes, a fundamental property of the Bayou design is that all serv-
ers move towards eventual consistency That is, the Bayou system guarantees that all servers eventually receive all Writes wa the pair-wise anti-entropy process and that two servers holding the
same set of Writes will have the same data contents, However, it cannot enforce strict bounds on Write propagation delays since these depend on network connectivity factors that are outside of
Bayou’s control. Two important features of the Bayou system design allows
servers to achieve eventual consistency. First, Writes are per- formed in the same, well-defined order at all servers. Second, the
conflict detection and merge procedures are deterministic so that servers resolve the same conflicts in the same manner.
as
In theory, the execution history at individual servers could vary
long as them execution was equivalent to some global Write
ordering. For example, Writes known to be commutative could be
performed in any order. In practice, because Bayou’s Write opera-
tions include arbitrary merge procedures, it is effectively impossi-
ble either to determine whether two Writes commute or to
transform two Writes so they can be reordered as has been sug-
gested for some systems [9].
When a Write is accepted by a Bayou server from a client, it is
initially deemed tentative. Tentative Writes are ordered according
to timestamps assigned to them by their accepting servers. Eventu- ally, each Write is committed, by a process described in the next
section. Committed Writes are ordered according to the times at
which they commit and before any tentative Writes.
The only requirement placed on timestamps for tentative Writes is that they be monotonically increasing at each server so
that the pair <timestamp, ID of server that assigned it> produce a total order on Write operations. There is no requirement that serv-
ers have synchronized clocks, which is crucial since trying to
ensure clock synchronization across portable computers is prob-
lematic. However, keeping servers’ clocks reasonably close is
desirable so that the induced Write order is consistent with a user’s
perception of the order in which Writes are submitted. Bayou serv- ers maintain logical clocks [20] to timestamp new Writes. A
server’s logical clock is generally synchronized with lts real-time
system clock, but, to preserve the causal ordering of Write opera-
tions, the server may need to advance its logical clock when Writes
are received during anh-entropy. Enforcing a global order on tentative, as well as committed,
Writes ensures that an isolated cluster of servers will come to
agreement on the tentative resolution of any conflicts that they
encounter. While this is not strictly necessary since clients must be prepared to deal with temporarily inconsistent servers in any case,
we believe it desirable to provide as much internal consistency as
possible. Moreover, clients can expect that the tentative resolution
of conflicts within their cluster will correspond to their eventual permanent resolution, provided that no further conflicts are intro- duced outside the cluster.
Because servers may receive Writes from clients and from other servers in an order that differs from the required execution
order, and because servers immediately apply all known Writes to their replicas, servers must be able to undo the effects of some pre- vious tentative execution of a Write operation and reapply it in a
different order. Interestingly, the number of times that a given Write operation is re-executed depends only on the order in which
Writes arrive via anti-entropy and not on the likelihood of conflicts
involving the Write.
Conceptually, each server maintains a log of all Write opera- tions that it has received, sorted by their committed or tentative timestamps, with committed Writes at the head of the log. The
server’s current data contents are generated by executing all of the Writes in the given order. Techniques for pruning a server’s Write
log and for efficiently maintaining the corresponding data contents
by undoing and redoing Write operations are given in Section 7.
Bayou guarantees that merge procedures, which execute inde- pendently at each server, produce consistent updates by restricting
them to depend only on the server’s current data contents and on any data supplied by the merge procedure itself. In particular, a
merge procedure cannot access time-varying or server-specific “environment” information such as the current system clock or
server’s name. Moreover, merge procedures that fail due to
exceeding their limits on resource usage must fail deterministi-
tally. This means that all servers must place uniform bounds on the CPU and memory resources allocated to a merge procedure and must consistently enforce these bounds during execution. Once these conditions are met, two servers that start with identical repli- cas will end up with identical rephcas after executing a Write.
6. Write Stability and Commitment
A Write is said to be stable at a server when it has